Computer Liquidator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A computer liquidator buys
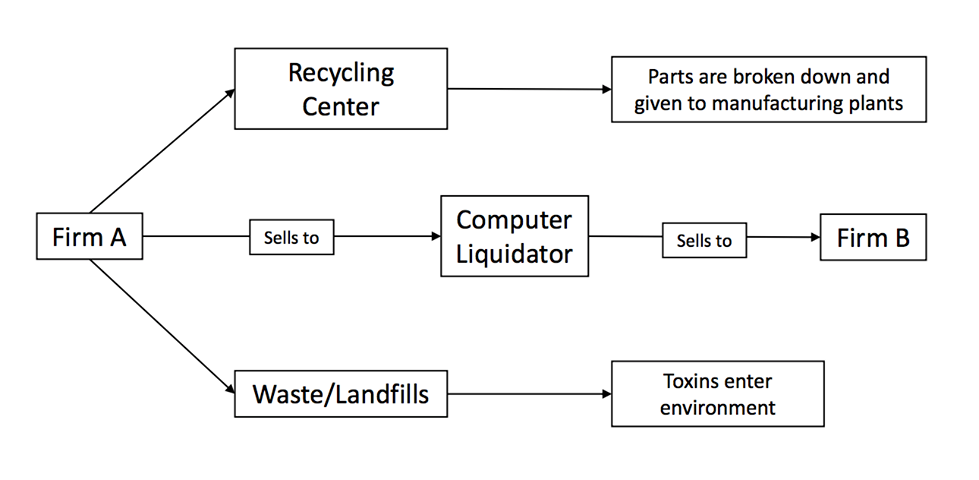 There are typically three agents in the computer liquidation process: the seller, the computer liquidator, and the buyer. The sellers are companies who are bankrupt and need to sell their assets, companies who are downsizing or expanding, and companies who are upgrading their technology. Usually, companies who are looking to sell their equipment will first conduct an
There are typically three agents in the computer liquidation process: the seller, the computer liquidator, and the buyer. The sellers are companies who are bankrupt and need to sell their assets, companies who are downsizing or expanding, and companies who are upgrading their technology. Usually, companies who are looking to sell their equipment will first conduct an
computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
technology and related equipment that is no longer required by one company, and resells ("flips") it to another company. Computer liquidators are agents that act in the computer recycling
Computer recycling, electronic recycling or e-waste recycling is the disassembly and separation of components and raw materials of waste electronics. Although the procedures of re-use, donation and repair are not strictly recycling, these are oth ...
, or electronic recycling, business.
There are several reasons why companies will sell, or liquidate
Liquidation is the process in accounting by which a company is brought to an end in Canada, United Kingdom, United States, Ireland, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign coun ...
, used Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system (I ...
(I.T.) equipment: bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor ...
, downsizing and expanding, or technological advancement. Technological advancement is the most common reason, as the equipment is no longer performing the tasks required of it, usually because it has been rendered obsolete by more advanced technology coming on to the market. This used or obsolete technology is often referred to as electronic waste
Electronic waste or e-waste describes discarded electrical or electronic devices. Used electronics which are destined for refurbishment, reuse, resale, salvage recycling through material recovery, or disposal are also considered e-waste. Informa ...
. Equipment designated as outdated for one company is still viable for another company, whose operations may not require advanced solutions. Often, an information technology audit
An information technology audit, or information systems audit, is an examination of the management controls within an Information technology (IT) infrastructure and business applications. The evaluation of evidence obtained determines if the inform ...
will be performed to help a company decide if their equipment needs updating, and if so, what the requirements are.
Reasons for Liquidation
Computer liquidation is a sustainable solution and isenvironmentally friendly
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that clai ...
. Rapid technology change, low initial cost, and planned obsolescence have resulted in a fast-growing surplus of computers and other electronic components around the globe. The purpose of computer liquidators is to keep as many computers and electronic parts out of landfills
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
. As newer and better technology replaces hardware at an ever-increasing speed, the amount of technical trash increases as the technology is being replaced. The speed at which hardware changes and innovates in the last few years follows, to some degree, Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
. Predictions were made that every landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
would soon be overflowing with discarded computer screen
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The di ...
s and computers, along with associated equipment such as keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
s and mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
s and all the other hardware associated with use of the Internet. Most electronic waste is sent to landfills or incinerated, which releases toxic materials such as lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, or cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
into the soil, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
, and atmosphere, thus having a negative impact on the environment. The best liquidating companies have clearly outlined policies regarding the disposal of dangerous substances which are often an issue with information technology.
The act of liquidation avoids the possible toxins and pollution that comes with putting electronic waste in landfills and also avoids the extra costs that go into recycling. For example, New York passed a law in 2015 that banned putting electronic devices in landfills. Now waste facilities in rural counties are being forced to either turn people away or eat the cost of recycling cathode ray tubes. Outside New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, counties are spending from $6 million to $10 million a year to deal with the problem, according to Stephen Acquario, executive director of the New York State Association of Counties. The option of liquidation actually incentivizes people to get rid of their electronic waste in a safer way, since recycling actually costs the owner money, so there are cases where people would rather throw it out to avoid the recycling fee.
Computer liquidators effectively create a secondary market to meet the demand of those who are looking for a cheaper solution and do not require cutting edge technology. It is important to note that the IT equipment being liquidated ranges from new technology to old technology. Because of the relatively lower price for secondary market equipment, some companies may even purchase tech devices from the secondary market to use as backups, stocking the equipment themselves preemptively so that a replacement is always on hand in the event of trouble. Product availability is also another reason for buyers to buy in this market. Manufacturers generally refresh their product line every 12 to 24 months, typically liquidating older products. But networking hardware can often see service lives of five years or more, and resellers and computer liquidators might carry products that are upwards of a decade old. End users that use a particular product may find it much easier and cheaper to add/replace an older device rather than take on the costs, business disruptions, and knowledge gaps that occur when upgrading to new products. When newer products are adopted, the used equipment is inevitably liquidated, thrown out or sold back, which creates a robust marketplace.
Process
 There are typically three agents in the computer liquidation process: the seller, the computer liquidator, and the buyer. The sellers are companies who are bankrupt and need to sell their assets, companies who are downsizing or expanding, and companies who are upgrading their technology. Usually, companies who are looking to sell their equipment will first conduct an
There are typically three agents in the computer liquidation process: the seller, the computer liquidator, and the buyer. The sellers are companies who are bankrupt and need to sell their assets, companies who are downsizing or expanding, and companies who are upgrading their technology. Usually, companies who are looking to sell their equipment will first conduct an information technology audit
An information technology audit, or information systems audit, is an examination of the management controls within an Information technology (IT) infrastructure and business applications. The evaluation of evidence obtained determines if the inform ...
to review their systems and equipment. The process is generally fueled by the supply side, as computer liquidators rely on what is available on the market for them to liquidate and resell. Thus, there nearly always exists a shortage for buyers.
Oceantech, for example, buys up computers, laptops, tablets and other such electronics from companies who no longer need the technology. They then conduct certified data destruction on the appliances. Technicians will then perform a thorough check of the systems and confirm that the devices are functional then they are stored into a warehouse. If only certain parts, like the motherboard or hard drives, are able to be used, these are stripped off of the machine and put into a warehouse to store. Then, the devices or parts are resold to smaller companies and places like school districts, who are in need of these products. Ocean Tech - Mike Satter, https://vimeo.com/166372141, Cool Places to Work. KMSP-TV, CH. 9, Fox Most of the companies involved in the computer liquidation business are also heavily involved in the computer and electronic recycling industry which takes on a similar process of disassembling and testing.
This process theoretically benefits both ends of the exchange, the seller gets money for equipment they no longer needs and the buyer gets cheap equipment that is necessary for their work.
Resources
A number of organizations have sprung up that provide technical guidelines to those handling or dealing in eWaste.References